Proteolysis in health and disease
Proteolysis fulfills essential functions in biological signal transduction and maintenance of proteostasis. Misregulated proteolysis is a major cause and driver of disease. Proteases are therefore popular drug targets, while cleaved proteins may provide for specific biomarkers of disease and treatment efficacy. We apply our degradomics approaches in collaborative work in the PhD research training school ProtPath and with other clinicians and clinical researcher to contribute to a better, systems-level understanding of physiological and pathological functions of proteases.
Proteolysis in renal signaling and disease
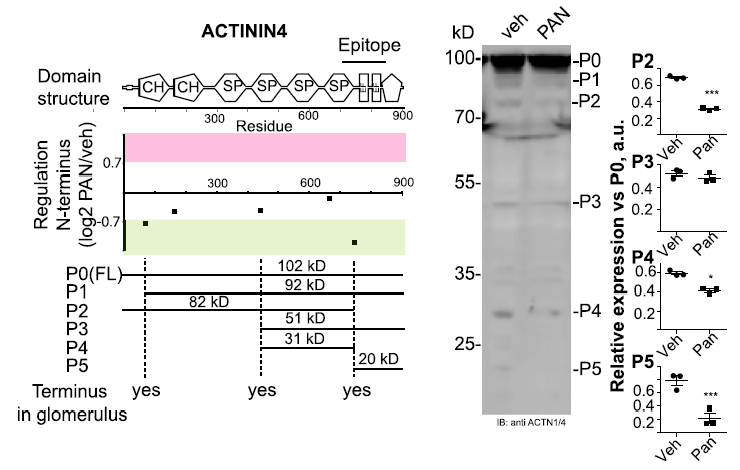
Our first N-terminome study of glomeruli revealed the existence of many proteolytically modified proteoforms. Treatment with puromycin aminonucleosid (PAN), a nephrotoxic agent that induces podocyte damage, activated caspases and induced altered processing of cytoskeletal proteins both in human podocyte cultures and in rats in vivo. We are now extending this work to other renal disease models, including a mouse model of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.
|
Publications from our collaboration with Nephrolab Cologne :
The proteome microenvironment determines the protective effect of preconditioning in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Kidney Int, 95:333-49.
The Podocyte Protease Web: Uncovering the Gatekeepers of Glomerular Disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 315:F1812-16
N-Degradomic analysis reveals a proteolytic network processing the podocyte cytoskeleton. J Am Soc Nephrol, 28: 2867-2878.
The proteome microenvironment determines the protective effect of preconditioning in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Kidney Int, 95:333-49.
The Podocyte Protease Web: Uncovering the Gatekeepers of Glomerular Disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 315:F1812-16
N-Degradomic analysis reveals a proteolytic network processing the podocyte cytoskeleton. J Am Soc Nephrol, 28: 2867-2878.
Proteolysis in cells exposed to mechanical stressAlmost every cell in our body is constantly exposed to mechanical stress. Together with our colleagues at IBI-2 at Forschungszentrum Jülich and other participants in the DFG-funded collaborative research unit 2743 "Mechanical Stress Protection" we aim to better understand the molecular mechanisms that help cells to maintain proteostasis in cells exposed to mechanical stress, and characterise the consequences of failure.
Further reading: For an overview, see Maintaining proteostasis under mechanical stress. EMBO Rep. 22(8):e52507. Overexpression of human BAG3P209L in mice causes restrictive cardiomyopathy. Nat Commun. 12(1):3575. Check also the webpage of FOR2743 for more detailed information. |