Degradomics
Proteomics is the ideal too to study proteases, the enzymes that sculpt the proteome, on a systems level. Dedicated methods allow us to zoom in on the peptides that reveal precise proteolytic cleavage sites, the N- or C-termini (e.g. using HUNTER/TAILS and CTAILS), or to profile protease specificity with proteome-derived peptide libraries (PICS).
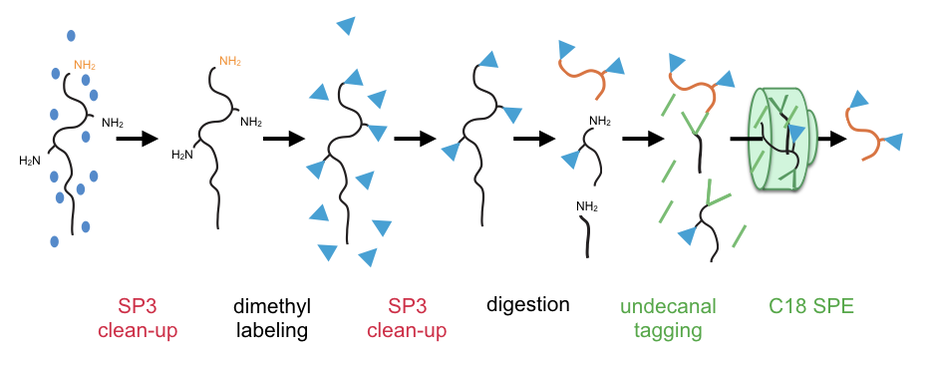
In collaboration with Philipp Lange´s lab at BC Children's Hospital Research Institute we have developed a robust, sensitive method for N-termini enrichment from limited samples, named HUNTER (High-efficiency Undecanal-mediated enrichment of N-TERmini).
We have also developed MaxQuant Advanced N-termini Interpreter (MANTI) as a software tool for convenient validation, annotation and visualization of N-terminome data analyzed by MaxQuant. The software is freely available for download.
Further reading
HUNTER publication in Mol Cell Proteomics, protocol in MiMB
MANTI publication in Analytical Chemistry, protocol in MIMB
Reviews on degradomics in J Exp Bot, Biochim Biophys Acta and New Phytol.
HUNTER publication in Mol Cell Proteomics, protocol in MiMB
MANTI publication in Analytical Chemistry, protocol in MIMB
Reviews on degradomics in J Exp Bot, Biochim Biophys Acta and New Phytol.
Novel digestion enzymes for proteomics
|
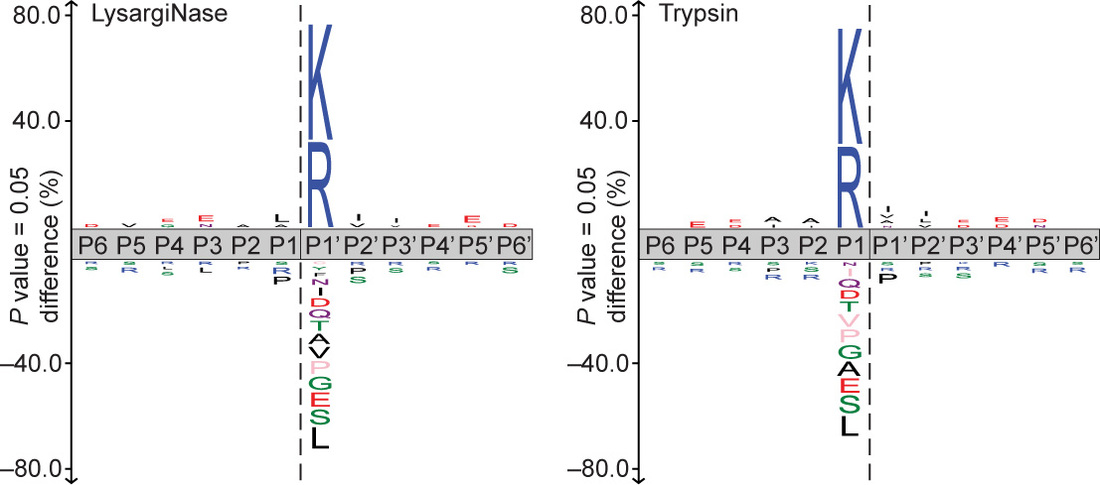
LysargiNase cuts selectively before arginine and lysine residues. Unlike the trypsin, LysargiNase-generated peptides therefore have N-terminal lysine or arginine residues leading to fragmentation spectra dominated by b-series ions. This improves protein C terminal–peptide identification and assignment of several arginine-rich phosphorylation sites. Notably, LysargiNase also cuts at methylated or dimethylated lysine and arginine, facilitating detection of these post-translational modifications.
|
Recombinant human legumain also turned out to be a very useful enzyme for proteomics. Cleaving specifically after Asp and Asn residues, legumain exteNDs protein sequence coverage and facilitates profiling of PTM sites invisible to trypsin. Legumain does not cut at Asn sites that are protected by glycosylation and can thus be used to assess the presence of this important PTM.
Further reading
Details on LysargiNase are published in Nature Methods.
Details on Legumain are published in Analytical Chemistry.
Details on LysargiNase are published in Nature Methods.
Details on Legumain are published in Analytical Chemistry.